Basic & Major Parts of Motherboard and its Functions
Basic & Major Parts of Motherboard and its Functions
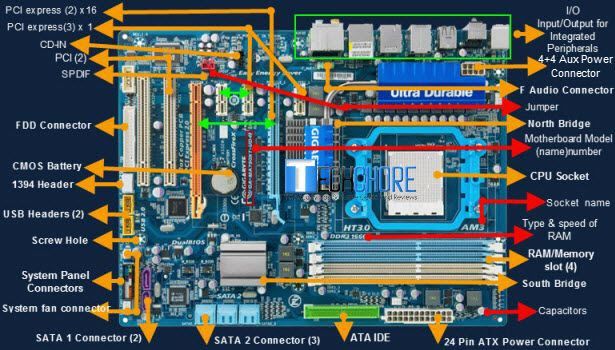
Parts of Motherboard
Parts of Motherboard. What is Motherboard? Motherboard is a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) with different hardware components on it.
It’s the electric conductor of the computer, responsible of distributing current and communication on each hardware components and chipset (CPU, RAM & etc.).
Motherboard is also often called as Planar board, MOBO, MB, Mainboard, System Board, Logic Board, Base Board and Backplane Board.
Basic Motherboard Components
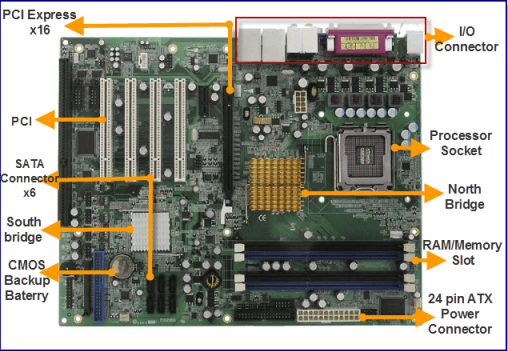
- Processor Socket
- North Bridge
- South Bridge
- RAM/Memory Slot x2
- 24 pin ATX Power Connector
- I/O ( Input Output)
- PCI express x16
- PCI
- SATA Connector
- CMOS Backup Battery
These are the basic parts of the Motherboard. Later we will discuss each functions. Knowing the basic parts of the Motherboard is important for all computer users. It may not be necessary but it will give you a big advantage.
For now, at least you know what a processor socket look like, where the 24 pin ATX Power Connector is situated. The difference between PCI and PCI express. Motherboard has two bridges the North bridge and the south bridge.What else? Your Motherboard has a tiny battery called CMOS Backup battery, the location of I/O, Memory slot and SATA connectors. Now let’s proceed to Major parts of Motherboard and its functions.
Major parts of Motherboard and their Functions

The major parts of Motherboard are a bit overwhelming compared to its basic components. However, these will give you a better knowledge and understanding about Motherboard.
- PCI Express x16 and x1
- CD-IN
- PCI
- SPDIF
- FDD Connector
- CMOS Battery
- 1394 Header
- USB Headers
- Screw Hole
- System Panel Connector
- SATA 1 Connector
- SATA 2 Connector
- ATA IDE
- 24 Pin ATX Power Connector
- Capacitors
- North Bridge
- South Bridge
- Memory Slot
- Type & Speed of RAM
- Socket Name
- CPU Socket
- Motherboard Model (name) number
- Jumper
- F Audio Connector
- 4+4 Pin Auxillary ATX Power Connector
- I/O Input/Output for Integrated Peripheral
PCI Express
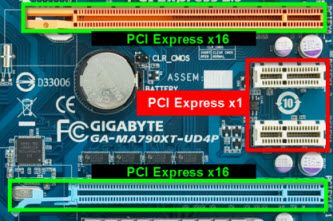
PCIe or PCI Express is one of the expansion slots on Motherboard. There were 4 types of PCI express x1, x4, x8 & x16 but only PCIe x1 and x16 remains popular until today. PCIe x16 is where GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) usually fits in. On the other hand PCIe x1 is recently used to hold PCIe SSD (Solid State Drive).

PCI Express replaced the AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) and it is also considered as PCI successor as well. PCIe x1 has a standard speed of 250 MB/s up to 3.9 GB/s while PCIe x 16 starts at 4GB/s up to 63GB/s.
CD-IN

CD-IN is a black-four-pin connector on Motherboard or Sound card. It is also known as Optical Drive Audio Connector. It’s being used to connect the four (4) pin wire from CD/DVD ROM to the CD-IN four (4) pin connector on MOBO/Motherboard.
PCI

PCI refers to Peripheral Component Interconnect and used to attach hardware components on Motherboard. Intel pioneered the introduction of PCI in 1992. It has both 32 bit and 64 bit versions with the speed of 133 MBps. Most hardware that fits in on PCI slot/s were sound card, LAN (Ethernet) card, Video card, USB port extension and etc.
S/PDIF

SPDIF (Sony and Phillips Digital Interconnect Format) is being used to connect audio equipment for digital audio transmission. It transmits compressed digital audio. Most Motherboards have this connector as well as sound cards and laptops. SPDIF can output digital audio through coaxial cable or fiber optic. For your information, SPDIF pins may vary. It is a good practice to check MOBO’s manual.
FDD Connector
 FDD (Floppy Drive Disk) header or connector is where the Floppy disk connects through a Floppy Drive cable. Floppy drive were not common today though it is still being used by some. It evolves from a floppy drive cable into a USB type.
FDD (Floppy Drive Disk) header or connector is where the Floppy disk connects through a Floppy Drive cable. Floppy drive were not common today though it is still being used by some. It evolves from a floppy drive cable into a USB type.CMOS Battery

CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) also known us Real-Time Clock (RTC) and NVRAM. It is powered by a 3 volts lithium battery. And it stores computer information such as; system time & date and system hardware settings.
IEEE 1394 Header

IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) 1394 Header is a standard interface for serial bus. Also known us i.LINK and FireWire. Capable of high-speed communications and real-time data transfer. Faster than USB 2.0 with the speed of almost 1 Gbps. 1394 Header resembles USB header, be careful not attached USB header cable into it or vice-versa. It may damage your Motherboard. Always check Motherboard’s manual.
USB Headers

USB header is a nine (9) pins header. It allows additional USB connection on your computer’s front/drive bay area. Motherboard already have a built-in USB ports at the I/O for integrated peripherals but additional can be added at the front bay that attached to USB header/s.
Screw Hole

Screw Hole or Mounting Hole it is where the Motherboard Case Standoff/Standouts fits in. To attached Motherboard into Computer case or chassis. Most of the Motherboard has 7 screw hole but it doesn’t mean that, all of it should be filled with standoffs. It’s a case to case basis, only insert standouts in screw hole that coincides chassis screw hole.
System Panel Connector

System Panel Connector also known us System Panel header, Front Panel and FPanel header is specifically meant to connect System panel Cables. To control or make Power Button, reset button, HDD LED and Power LED works. Take note: Colored System panel cables are positive or powered wire while black or white wires are the ground or negative wires. The wire colors, cables and connector may be different from each Motherboard brands and chassis, so always check the manual.
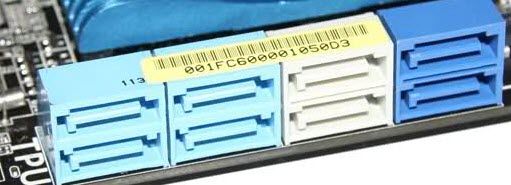
SATA 1 connector

SATA 1 is the first generation SATA interface with the speed of 1.5 Gbps. It is officially known as SATA 1.5 Gbps. It has a bandwidth throughput of up to 150 Mbps. This is the successor of P/ATA or IDE type connector.
SATA 2 Connector
SATA 2 is the second generation SATA interface with the speed of 3.0 Gbps. It is officially known as SATA 3.0 Gbps. It has a bandwidth throughput of up to 300 Mbps. SATA 2 are usually located at the side of the Motherboard.
ATA IDE

ATA (AT Attachment) IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics or IBM Disc Electronics) also known as PATA (Parallel ATA). It is used to be the standard interface for IDE compatible hard drives but is now replaced by SATA.
24 Pin ATX Power Connector

ATX 2 introduced the 24 Pin ATX power connector replacing the 20 pin power connector. It is through ATX power connector that the Motherboard gets power from Power Supply. Thus, distributing current and voltage to all Motherboard components.
24-pin ATX power cable can be used to connect into 20-pin ATX power connector by leaving the four (4) pins aside. However, 20-pin ATX power cable will not work on 24-pin ATX power connector, 24-pin ATX power cable should be used.
In most cases the 20 or 24 pin ATX power cable are supported by 4-pin or 8-pin ATX 12Volts secondary.
Capacitors

Motherboard capacitors are small components on Motherboard that helps condition power on other Motherboard components. Capacitor can also store electronic charge, therefore it is advisable not to touch one if the computer has just turned off. To release the capacitor electronic charge, press the computer power button while it is unplug. Bulge capacitors may cause different problems on Motherboard.
NorthBridge
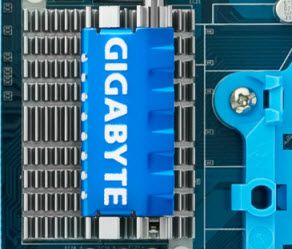
Northbridge also known as NB or PAC it controls the flow of communications among Processor, PCIe and RAM or Memory stick.
Southbridge

Southbridge is a Motherboard IC that takes care all I/O controller, integrated hardware and hard drive controller. Integrated peripherals may include sound card and video card, USB ports, SATA, IDE, BIOS, Ehternet, Firewire and etc.
Memory Slot

Memory Slot also known as RAM slot or Memory socket it is where the RAM or Memory stick is inserted. Standard Motherboard used to have two Memory slots but high-end Motherboards may have more.
Type & Speed of RAM

This information is vital, it is important to know what speed and type of RAM does the Motherboard support. The sample above explains that the Motherboard is compatible with DDR3 RAM with 1666+ MHZ. So, DDR and DDR2 RAM will not fit the Motherboard. However, any DDR3 RAM will work even if it has a lower or higher MHZ like 1066, 1333, 1600, 1800. But it is advised to follow the recommended MOBO’s required RAM speed and type to maximize its performance.
Socket Name

Socket name is another important information to look into in Motherboard. This is to make sure that the processor is compatible with the Motherboard. The image above is sample of AMD AM3 socket. AMD also has socket FM1, socket FM2, AM3+, AM2, AM2+ and AM4 is the latest. Intel used to have LGA 775, LGA 1156, LGA 1366, LGA 1150, LGA 1151 and LGA 1155.
CPU Socket
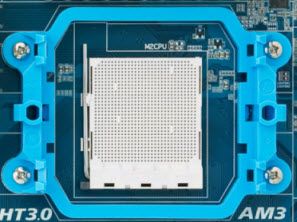
CPU Socket it is where the Processor or CPU (Central Processing Unit) is fit in. The processor should be compatible with Motherboard socket as the Socket Name mentioned above.
Motherboard Model (name) number

Motherboard Model name & number is another information worth knowing. This is important especially if the Motherboard drivers were misplaced or lost. By typing the Motherboard model number followed by drivers (GA-MA790XT-UD4P drivers) into search engine or manufacturer site, it will help to find the correct drivers for the Motherboard on the internet.
Jumper/s
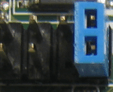
Jumper/s are used to close or allow current flow into certain board sections. It also used to configure hardware components such as; hard drive, BIOS, CD ROM, DVD ROM, Modem, Sound card and etc. On IDE days, it was used to adjust master drive, slave drive and cable select by moving the jumper between each two pins.
F Audio Connector
F Audio Connector is use to connect Front Audio Jacks via case connector. This is an extension of I/O integrated Audio jacks.
4+4 Pin Auxillary ATX Power Connector

12V ATX 4 or 8 pins power is used to provide 12V to the processor voltage regulator. Normally, 12V ATX power connector has only 4 pins. However, in some cases there were Motherboards that has a 4+4 (8) pins.
The good thing is, if your power supply only has 4 pins, it will still work just leave the other 4 connector vacant. Same goes to, if your power supply has 8 pins and the Motherboard only has 4, just split it apart to make two (2) 4 pins. Then, leave the other 4 pins and plug the other 4 into the Motherboard.
I/O Input/Output for Integrated Peripheral

I/O Input Output for Integrated Peripherals is a Motherboard’s built-in external connector. It is where the Mouse, keyboard, monitor, USB cable, Firewire, SPDIF, Audio jacks and other external devices are to be connected.
Comments
Post a Comment